Changes in Temperature and Ph on Enzyme Activity by Breaking
Maltose was present in all test tubes. Competitive inhibitors compete with the substrate and block the active site and non-competitive inhibitors bind at an alternative site on the enzyme which causes the enzyme to change shape so that the.
Effect Of Temperature And Ph On Enzyme Activity Definition Examples Diagrams
It most likely will cause a change of the active site preventing the specific substrates from binding to it undergoing a conformational change and producing the final products.

. A continued increase in temperature results in a sharp decrease in activity as the enzymes active site changes shape. Chitosanase activity from T. The correlation of pH doesnt seem as clear.
Answer 1 of 3. When the temperature rises too high in enzyme-controlled reactions the change in the active site is irreversible. It can affect the intramolecular forces and change the enzymes shape -- potentially to the point where it is rendered ineffective.
For example alpha amylase which found in the mouth operates most. We say that the enzyme has been denatured. How pH affects amylase activity.
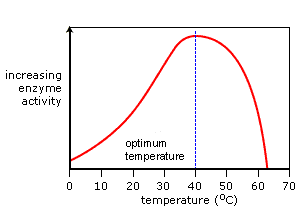
Low temperatures slow enzymes and substrates down which reduces collisions between them. Figure 2 The effect of pH and temperature on the activity of an enzyme. In this investigation you will explore how these two environmental conditions affect enzyme activity by measuring the rate at which O 2 is produced when H 2 O 2 is exposed to catalase at differ-ent pH levels and temperatures.
When pH of a particular medium changes it leads to an alteration in the shape of the enzyme. Changes in pH or temperature decrease enzyme activity because bonds b. Changes in temperature can.
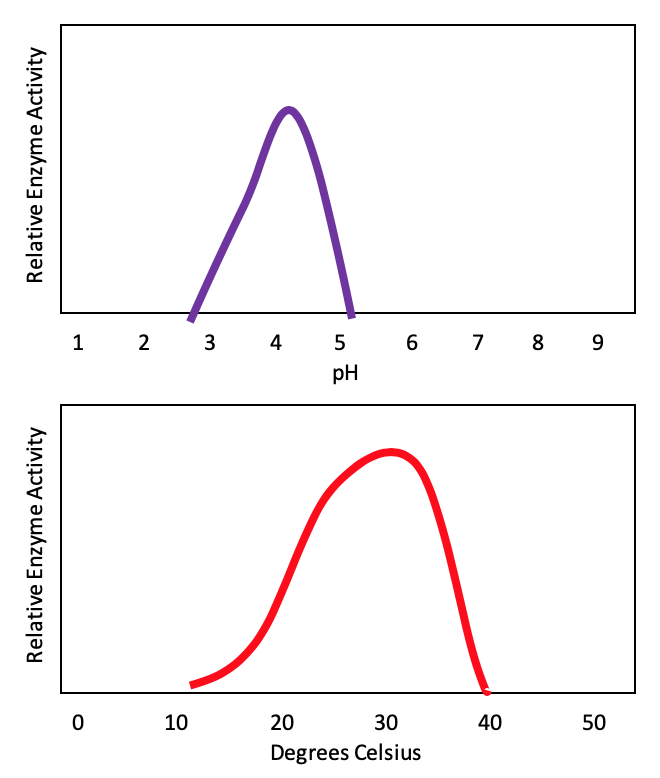
Polysporum chitosanase activity was also strongly affected by pH values with a sharply increase for values above 52. Effects of pH Changes in pH also alter the shape of an. Test tubes 2 and 3 which contained pH 5 and 6 starch completed the reaction at the same time.
Temperature affects enzyme activity in three ways. Amylase is shown in blue in both graphs. Our group got curious about how changes in temperature and pH levels affect enzyme activity.
How does pH affect enzyme. Both acidic and basic pH can cause enzymes to denature because the presence of extra H ions in an acidic solution or OH- ions in a basic solution can modify the chemical structure of the amino acids forming the protein which can cause the chemical bonds holding. The optimum temperature for amylase is close to 37ºC which is human body temperature.
To make the extraction buffer for the peroxidase enzyme mix equal volumes of 01 M sodium phosphate monobasic and 01 molar sodium phosphate dibasic solutions to achieve a final volume of 500 mL. Mar 4 2018 The pH of a solution can impact the enzyme because enzymes are composed of amino acid chains that have functional groups. Since enzymes are group of protein and protein can break easily by acid base and hot temperature.
This means the key will no longer fit the lock. Environmental conditions such as temperature or pH level can affect the function of enzymes. With these effects in mind typical enzymes have a pH range in which they perform optimally.
Changes in pH and temperature can decrease an enzymes activity by breaking the shape or denaturing the shape of the biological catalyst enzyme. High temperatures and changes in pH change the shape of denature enzymes. Denaturing enzymes If enzymes are exposed to extremes of pH or high temperatures the shape of their active site may change.
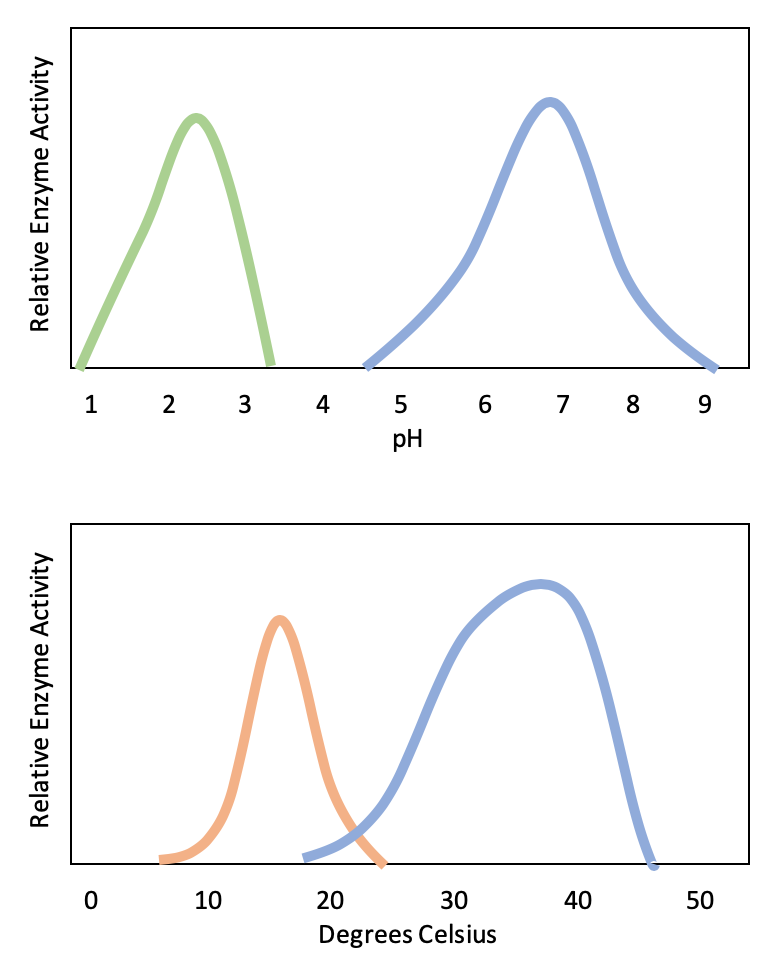
Temperature - The higher temperature destroy the structure of the protein thus reduces the activity of enzymes and the. Top Amylase blue has an optimum pH of about 7. PH - Any change in the pH alter the structure of the protein thus affects the activity of the enzymes.
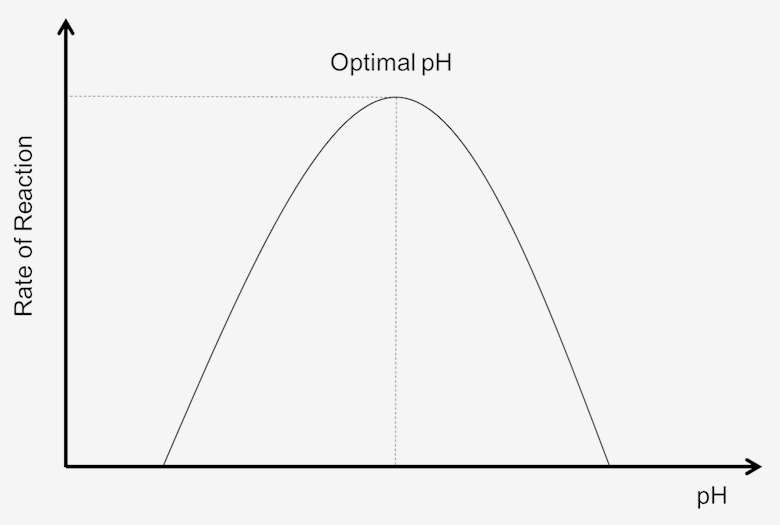
The change in pH will change the bonding patterns and as a result increased changes from the optimum pH will result in the shape of the active site changes. Within a narrow pH range changes in the structural shapes of the enzymes and substrates may be reversible. Investigating the Effect of pH and Temperature on Peroxidase Activity.
H2O2 is a natural by-product and toxic. Factors that affect enzyme activity include pH enzyme concentration and substrate concentration. In addition to high temperatures extreme pH and salt concentrations can cause enzymes to denature.
Temperature affects enzymes by increasing the bond energy causing the atoms in the enzymes bonds to drift apart from each. But for a significant change in pH levels the enzyme and. The green enzyme which has an optimum pH of about 23 might function in the stomach where it is very acidic.
Figure 2 shows the reaction rates of the different pH levels. Enzymes show a temperature optimum. KoningiiI was also strongly affected by pH and enzyme activity was enhanced at pH values above 50 presenting maximal values around pH 55 and temperature in the range of 4050C.
A pH environment has a significant effect on an enzymes. When H2O2 contacts catalase it breaks down into water and oxygen. However the effect of bond breaking will become greater and greater and the rate of reaction will begin th decrease.
These functional groups are vulnerable to changes brought on by surrounding charges. As temperature increases initially the rate of reaction will increase because of increased kinetic energy. Changes in pH or temperature decrease enzyme activity because bonds break and the enzyme returns to its tertiary structure.
Test the resulting solution using a pH meter. Not only enzymes the pH level may also affect the charge and shape of the substrate. So it causes a far more drastic change in the rate of reaction.
It is now denatured. The Effects of Temperature on Enzyme Activity. If this happens then the substrate will no longer fit into the enzymes.
Changes In Enzyme Activity Mhcc Biology 112 Biology For Health Professions
Effect Of Ph On Enzymatic Reaction Creative Enzymes
Changes In Enzyme Activity Mhcc Biology 112 Biology For Health Professions
No comments for "Changes in Temperature and Ph on Enzyme Activity by Breaking"
Post a Comment